7 Facts About Rip Currents: The Invisible Danger of the Surf Zone
Rip currents are powerful, fast-moving channels of water that flow from the shore back out to sea. These currents are one of the most common dangers at the beach but are often misunderstood. This blog explores what rip currents are, how they form, their causes, types, and dangers, and provides tips on how to stay safe. By gaining a deeper understanding of these natural phenomena, beachgoers can make better choices and reduce their risk of danger in the surf zone.
Table of Contents
- What Are Rip Currents?
- What Causes Rip Currents?
- Why Are Rip Currents Dangerous?
- How to Identify Rip Currents
- Components of a Rip Current
- Types and Sizes of Rip Currents
- How to Stay Safe
- Advanced Detection and Safety Measures
- Fascinating Facts About Rip Currents
- How Rip Currents Form
- Tips for Avoiding Rip Currents
- Final Thoughts
- Get Involved with ISLA: Support International Lifeguard Development and Beach Safety
What Are Rip Currents?
Rip currents are narrow, fast-moving channels of water that push away from the shore. These currents are most often found at surf beaches, particularly where waves break over sandbars, reefs, or near piers and jetties. While rip currents can occur in oceans, they can also form at large freshwater bodies, like the Great Lakes. Even experienced swimmers can find themselves in danger if caught in one. Understanding the behavior of these currents is crucial for both swimmers and lifeguards to avoid accidents.

What Causes Rip Currents?
The formation of rip is primarily driven by wave action. As waves break over the shore, they push water toward the land, creating a buildup. To release this excess water, it flows back toward the ocean, often finding narrow paths between sandbars, reefs, or structures like piers. The key contributing factors include:
- Wave Action: Stronger waves generate more water moving toward the shore, increasing the potential for rips.
- Beach Morphology: The shape and structure of the beach and underwater features, such as sandbars and troughs, influence where these currents form and how strong they are.
- Multi-feeder & One Feeder: Rip currents can have one main source or multiple sources of water channeling in. One feeder rips are more common.
- Tidal Changes: As the tides rise and fall, the water flow can intensify, contributing to the development of rips.
- Weather Conditions: Storms and high winds can alter the beach profile and generate new currents, often making the water more dangerous.
- Man-Made Structures: Piers, jetties, and groins can disturb natural water flow, creating rips on their leeward sides.
- Beach goers: Humans can also disturb natural water flow, and bottom sand conditions creating feeder currents that can lead to the creation of rips.
Why Are Rip Currents Dangerous?
Rip currents are hazardous because they can quickly carry swimmers far away from shore. Some of these currents are extremely fast, moving at speeds that exceed the swimming speed of even the strongest swimmers. A swimmer caught in one may panic and exhaust themselves, further increasing the risk of drowning. Statistics show that rips cause more than 100 deaths each year in the U.S. and account for over 80% of surf rescues made by lifeguards. Understanding the risks is crucial for anyone spending time at the beach.
How to Identify Rip Currents
Being able to spot rip currents can significantly reduce your risk of getting caught in one. Look for the following signs:
- A gap in the breaking waves, which may appear as a darker, smoother patch of water.
- Churning or choppy water that moves seaward, often carrying foam, seaweed, or debris.
- A noticeable color difference between the current and the surrounding water.
- Faster-moving water moving outward, particularly when it’s calmer than the surrounding area.
Before entering the water, always observe the conditions and check if there are any posted warnings, flags, or advisories for rip currents. Lifeguards are an excellent resource for safety advice and can point out areas of concern.
Components of a Rip Current
- Feeder: The “feeder” of a rip current is the portion where the water is directed from the shore toward the main current. This area is typically found near the breaking waves, where the water flows back into deeper areas of the ocean. It is essential to recognize the feeder, as it can look like a narrow, concentrated stream of water moving seaward. The water in this area can flow quickly, carrying any debris or sand in its path. Understanding the flow dynamics of the feeder is crucial for lifeguards and beachgoers alike, as it helps to predict how the rip current may develop and where it will be strongest.
- Neck: The “neck” of the rip current is the narrowest, most concentrated part of the current. It occurs after the water has gathered in the feeder, where the flow funnels into a more defined path. This is where the current’s speed is greatest, making it the most dangerous section. The neck can extend several meters offshore, and its strength can often be underestimated by swimmers who think they are just in a small inlet. It’s important to note that, while the neck is usually marked by choppy water and foamy whitewash, it may not always be immediately visible from the shore. Lifeguards should be vigilant in identifying the neck to prevent swimmers from entering it unwittingly.
- Head: The “head” of the rip current marks its endpoint, where the water flows out into deeper ocean water beyond the breaking waves. While this part of the rip current is less hazardous in terms of speed, it can still be dangerous because it leads out to an area where the swimmer could be pulled further from shore if they are not cautious. Often, the head is harder to identify than the feeder and neck, but it’s still essential for swimmers to avoid being pulled into this deep-water section. Understanding the flow from the head back to the open ocean helps lifeguards assess how strong the overall rip current may be and aids in making crucial safety decisions.
Types and Sizes of Rip Currents
Rip currents vary in their characteristics, including size, shape, and duration. Some are long-lasting, while others may appear and disappear in a matter of minutes. The type and strength of the current depend on various factors such as wave height, underwater features, and weather conditions. Here’s a breakdown:
Types of Rip Currents
- Fixed Rip Currents: These currents are stable and occur on sandy beaches in the same location due to consistent underwater features like sandbars. When surf conditions change, fixed rip conditions may also change due to the movement of the sand. Fixed rips may last hours, days, or even months.
- Flash Rip Currents: These currents can form quickly and often disappear just as fast. They may result from a single large wave or sudden changes in wave conditions.
- Moving Rip Currents: Similar to flash rip currents, except these rips move along the beach, usually with the prevailing winds and surf direction due to the displacement of the sand after below after set waves. These rips can wreck havoc on beachgoers as they move along the shoreline pulling large numbers of people into deeper water.
- Mega Rip Currents: These are large currents that can span the width of multiple normal rip currents. They typically occur during high swell events or after storms.
- Permanent Rip Currents: These currents are influenced by man-made or natural coastal structures such as piers, jetties, reefs, or groins. Water piles up on one side, forcing a powerful flow on the other side.
Size Variations
Rip currents can vary widely in their dimensions:
- Width: Some currents are narrow, extending only a few meters, while others can stretch over 40 meters across.
- Length: These currents may travel just beyond the surf zone or continue hundreds of meters offshore.
- Speed: While some rip currents move at 0.5 meters per second, others can reach speeds in excess of 2 meters per second.
- Depth: Rips can form in shallow water but often extend several meters deep where the waves do not break.
How to Stay Safe
While rip currents can be dangerous, knowing how to stay safe can make a huge difference. Here are some essential tips to follow when at the beach:
- Swim Near Lifeguards: Always choose beaches that have lifeguard supervision, as they can respond quickly in case of an emergency.
- Learn to Spot Rip Currents: Observing the water before entering is key. Pay attention to the wave patterns and look for any signs of potential rip currents.
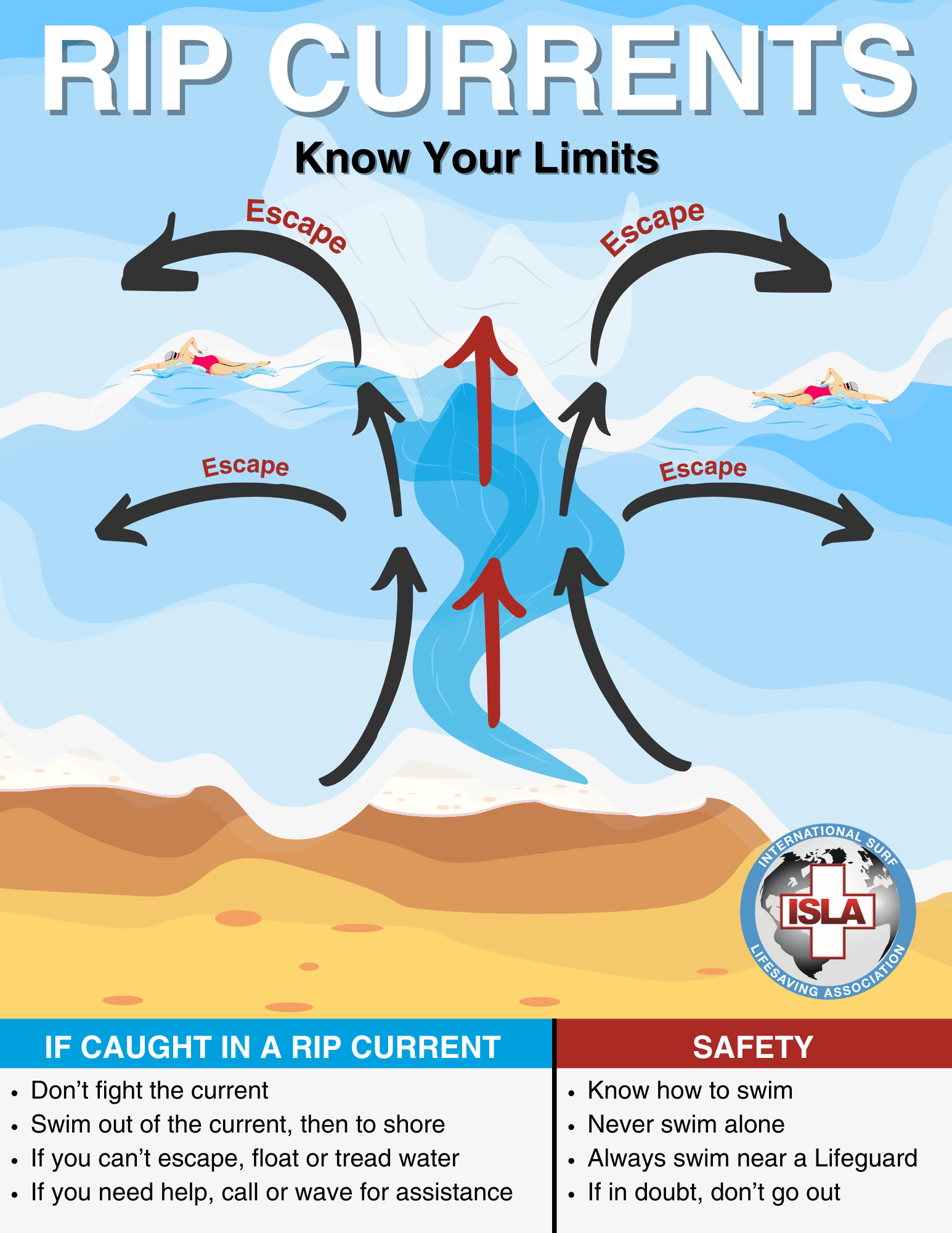
- Don’t Fight the Current: If you are caught in a rip current, remain calm and avoid panicking. Try swimming parallel to the shore to escape.
- Use Floatation Devices: Make sure to have a floatation device with you when entering the water, particularly if you’re unfamiliar with the conditions.
If Caught in a Rip Current:
- Stay Calm: Rip currents typically do not pull swimmers under the water.
- Swim Parallel: Swim across the current to escape its pull. Once free, swim toward the shore.
- Signal for Help: If you’re unable to escape, signal for help by waving your arms and shouting.
Rescuing Others:
- If you see someone caught in a rip current, immediately alert a lifeguard or call 911.
- If you cannot safely perform a rescue, throw them a floatation device and wait for trained professionals to respond.
Advanced Detection and Safety Measures
Modern technology is helping lifeguards and coastal authorities improve safety measures and save lives. Drones, equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging, are now being used to detect rip currents in real-time and monitor large stretches of coastline more efficiently than ever before. Artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced monitoring systems analyze wave patterns, currents, and other environmental factors to predict dangerous conditions and provide early warnings to beachgoers.
Many beaches have implemented real-time forecasting systems and rip current alerts based on a combination of weather, wave, and tide data, accessible via mobile apps, websites, and even electronic signage at the beach. These tools not only enhance the ability to identify and respond to rip currents but also improve public education by raising awareness about beach safety. Together, these innovations are playing a significant role in reducing beach-related incidents, empowering both lifeguards and beachgoers to make safer decisions.
Fascinating Facts About Rip Currents
- They Don’t Pull You Under: Rip currents do not pull swimmers beneath the water; they only carry them out to sea.
- Speed: While some currents move at average speeds of 1-2 feet per second, others can reach up to 8 feet per second.
- Global Phenomenon: Rip currents are not confined to oceans. They also occur at lakes, such as the Great Lakes, where similar conditions can create powerful currents.
- Variability: The size and strength of rip currents can change depending on the weather, tide, and wave conditions.

How Rip Currents Form
Rip currents are formed when the breaking waves create variations in water pressure and flow. Water moves toward the shore with the waves and then seeks a way to return to the sea. This movement often funnels through areas where there is less resistance, such as gaps between sandbars, reefs, or near structures. Various factors like the shape of the coastline, the power of the waves, and the tides all influence where and how rip currents form.
Tips for Avoiding Rip Currents
- Check Beach Conditions: Many beaches post signs or flags indicating dangerous water conditions. Always check before swimming.
- Consult Lifeguards: Ask lifeguards about the safest areas to swim and whether any dangerous currents have been reported.
- Stay Aware: Always monitor the movement of water while in the surf zone. If conditions seem to change suddenly, be prepared to exit the water.
Final Thoughts
Understanding rip currents—how they form, their causes, types, and how to react—can save lives. Whether you’re a seasoned swimmer or a first-time beachgoer, it’s crucial to respect the ocean’s power. Before heading into the water, consult lifeguards and stay informed about current conditions.
For more lifesaving tips, powerpoints, signs and information, visit the United States Lifesaving Association website. Stay safe, stay informed, and enjoy the beach responsibly.
For beach safety updates and tips, you can also check out this National Weather Service page on rip currents.
Get Involved with ISLA: Support International Lifeguard Development and Beach Safety
At ISLA, we believe that together, we can make a profound difference in the global fight against drowning and enhance beach safety everywhere. Whether you’re a seasoned lifeguard, someone with a deep passion for beach safety, or an individual looking to make a positive impact, there are many ways you can get involved. Volunteering for one of our lifeguard development operations allows you to work directly with local communities in need, providing them with critical lifesaving training, equipment, and resources. Volunteer and be part of the solution, helping to save lives in some of the most vulnerable coastal areas worldwide.
One of the best ways to deepen your involvement with ISLA is by becoming a certified lifeguard through our International Beach Lifeguard Academy. Our academy offers specialized training for individuals seeking to enhance their skills and become leaders in beach safety. By completing our rigorous training programs, you’ll earn ISLA certification, recognized worldwide for its high standards and commitment to professional lifesaving practices. Becoming a certified ISLA lifeguard not only equips you with the skills to save lives, but it also helps you contribute to the global mission of improving beach safety. Learn more about our academy and certification process to start your journey as a globally certified lifeguard.
If your organization is in need of lifesaving training, equipment, or consulting services, ISLA is here to help. With years of experience in lifeguard development and training programs, we can provide tailored services that address the specific needs of your beach or community. We’re committed to advancing lifesaving standards around the globe. By requesting ISLA services today, you’ll gain access to a network of experts and resources that can help you build a stronger, more effective lifeguard program.
Joining ISLA as a member is another powerful way to support our mission and make a difference. Our members form a dedicated community committed to advancing lifesaving practices on a global scale. As a member, you’ll receive exclusive access to updates, training resources, and the chance to be part of our life-saving initiatives worldwide. Become a member of ISLA today and join a movement that’s saving lives and transforming the future of beach safety.
In addition to membership, there are many other ways you can support our mission. Want to wear your support proudly? Visit our store and shop for exclusive ISLA merchandise. All proceeds from our store go toward funding our lifesaving operations, helping to provide training, equipment, and resources to communities in need. Staying informed is also vital. Sign up for our newsletter to receive the latest updates on ISLA operations, beach safety tips, and news about how you can get involved in our mission.
Finally, follow us on social media to stay connected with the ISLA community. Sharing our posts helps spread the word about the importance of beach safety and lifesaving initiatives worldwide. Your support—whether through volunteering, membership, donations, or simply spreading awareness—makes a significant impact. Every action you take helps advance our mission, and together, we can continue to make beaches safer for everyone. Follow us on social media and help us amplify our global reach!